It’s no secret the world is turning green.
People are gravitating toward renewable energy sources, such as solar panels, which are part of the green revolution. This is because green energy is environmentally friendly, saves money and becoming relatively cheap.
Other than that, installing a grid-tied solar system will increase your property value while eliminating some or all of your utility bills.
The most common renewable energy option for the homeowner is the grid-tied solar power system.
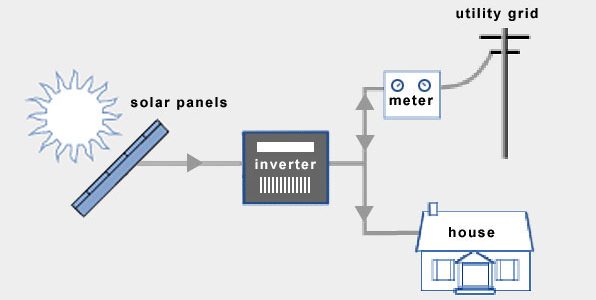
The grid-tied solar system is a type of solar system permanently connected to the electrical power grid. Grid-tie does not require batteries, as in the case of off-grid solar systems. Grid-tie solar systems allow the home to use solar energy when available, or to channel excess power back into the grid.
How does grid tied solar work?
Before delving into the working mechanism of grid tie, it is essential to mention that the system is linked to an electrical grid and cannot function in its absence. Thus, for the system to work, the grid should be working as well.
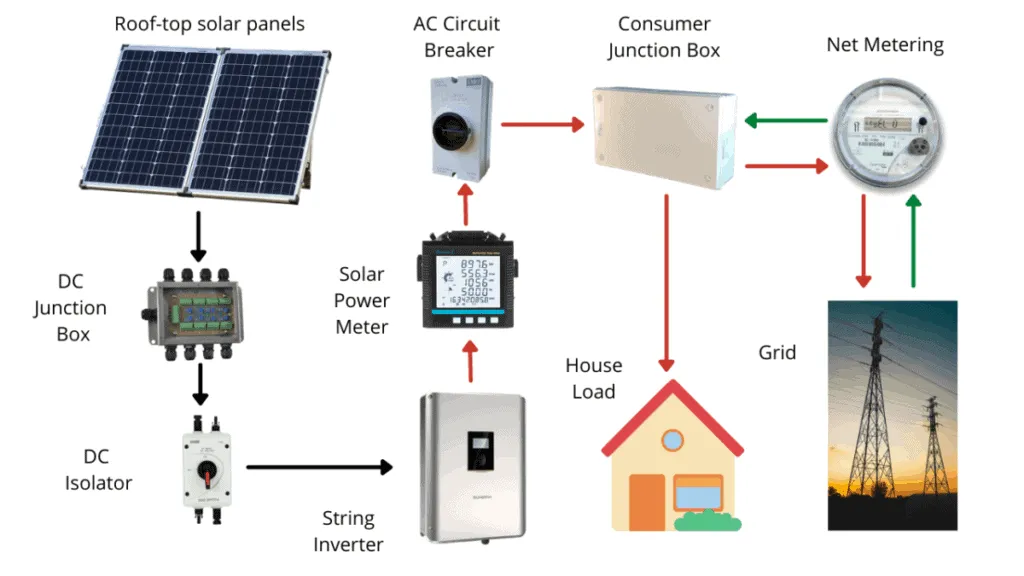
The grid-tie solar system is composed basically of an energy (net) meter, one or multiple inverters, and solar panels.
Solar panels, usually installed on a rooftop or open space, convert rays from the sun into direct current electricity through the photovoltaic process. For the conversion of produced electricity into alternating current, the grid-tied system needs an inverter.
The inverter is an instrumental part of the whole system as it changes DC electricity from the panels into the power grid frequency, which is either 50 or 60Hz, depending on the continent.
DC electricity from solar panels goes into the inverter that is in turn connected to the distribution board.
This is quite different from the off-grid system, where DC electricity is stored in batteries directly, before being fed to the inverter. In this case, electricity gets fed straight into the grid.
Components of a grid-tie solar system
Diagram – The basic components of a grid-tied solar power system
What does a solar inverter do?
Solar panels generate direct current or DC. Direct current is not ideal for home use as it is susceptible to power loss and attracts high maintenance costs. Of course, modern appliances use only AC, so conversion is required.
However, solar panels are not able to convert the DC to AC on their own. This is where the solar inverter comes in.
Older solar systems had just one central inverter and later converted to the more efficient string-inverter.
A string-inverter converts the voltage from several solar panels connected in a single array, and there may be several of these in a large installation.
A big problem with central and to some extent string inverters, are shading losses. When one or more panels are shaded, the output of the rest of the system is severely reduced.
Micro-inverter protection against shading losses
This problem is largely overcome by the installation of micro-inverters. Micro-inverters convert DC to AC at the panel level and are connected to the back of individual panels. Some micro-inverters can accommodate several panels.
olar Panels
Solar panels feature photovoltaic (PV) cells that are silicon-based. The PV cells are capable of converting irradiance from the sun into DC electricity.
Cells within the panel interconnect to one another through tiny cables. For efficiency, solar panels are connected together to create a solar array known as a string. A system may have several strings.
The potential amount of electricity every array can produce is subject to losses linked to shading, tilt angle, orientation, and the efficiency of individual panels.
Infographic: 10 Solar PV System Losses

A good quality solar panel will produce electricity when it is sunny and also be productive during overcast or cloudy weather. This will depend on the height or thickness of clouds.
Another crucial attribute that impacts the power output of a solar panel is the sun’s irradiance. Irradiance is the amount of light energy falling on the panel mesured in kWh/m2/day or year, also known as Peak Sun Hours(PS
Solar panels use the sun’s irradiance to produce electricity and not its heat.
How does net-metering work in a grid-tied solar system?
To enjoy net metering services courtesy of the grid-tied solar system, you need a power meter. It also goes by the name net meter or the two-way meter, owing to its ability to account for power going in both directions.
No responses yet